
The atria will be activated in the opposite direction, which is why the P-wave will be retrograde. In both cases listed above the impulse will originate in the junction between the atria and the ventricles, which is why ectopic beats and ectopic rhythms originating there are referred to as junctional beats and junctional rhythms.

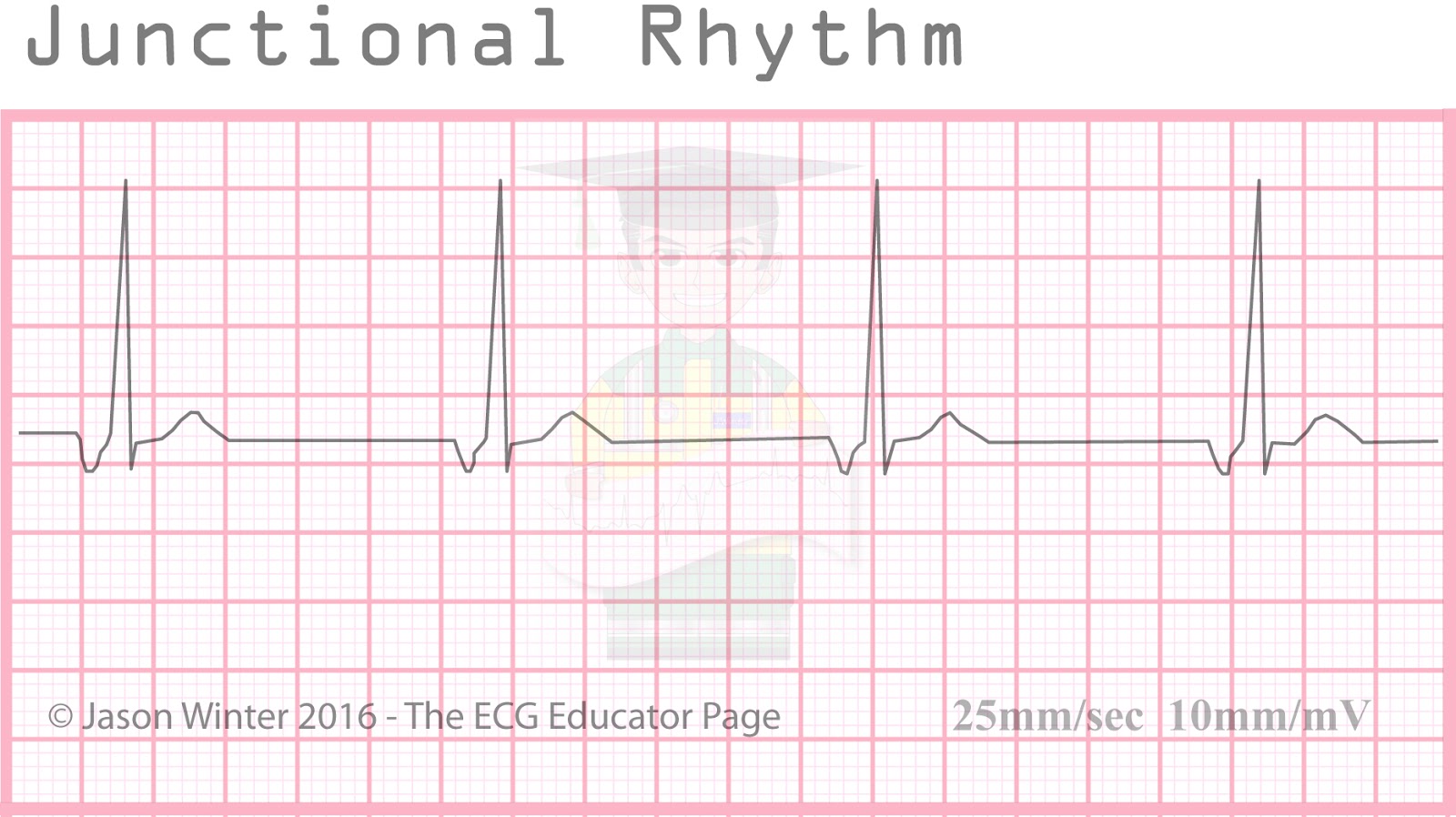
Junctional tachycardia is less common. Basic knowledge of arrhythmias and cardiac automaticity will facilitate understanding of this article.Īs discussed in Chapter 1 the atrioventricular node does not exhibit automaticity, meaning that it does not discharge spontaneous action potentials, at least not under normal circumstances. The most common rhythm arising in the AV node is junctional rhythm, which may also be referred to as junctional escape rhythm. In this article, you will learn about rhythms arising in, or near, the atrioventricular (AV) node. QRS Complex: Usually normal in duration and morphology, less than 0.12 seconds.Rhythms arising near the atrioventricular node: junctional rhythm (escape rhythm) and junctional tachycardia.P-R interval: If the P wave occurs before the QRS complex, the interval will be less than 0.12 seconds.They will be inverted, and may appear before or after the QRS complex, or they may be absent, hidden by the QRS.

P waves: Depends on the site of the ectopic focus.Rhythm: Irregular in single junctional escape complex regular in junctional escape rhythm.digoxin toxicity), a pathological slowing of the SA discharge, or a complete AV block. Cause Ī junctional escape complex is a normal response that may result from excessive vagal tone on the SA node (e.g. This rhythm can usually be tolerated if the rate is above 50 beats per minute. Therefore, the person may exhibit signs and symptoms similar to other bradycardia such as lightheadedness, dizziness, low blood pressure, and fainting. Junctional rhythms (if a bradycardia) can cause decreased cardiac output. It can also occur following a premature ventricular contraction or blocked premature atrial contraction.
Activity for junctional escape rhythm series#
It is a protective mechanism for the heart, to compensate for the SA node no longer handling the pacemaking activity, and is one of a series of backup sites that can take over pacemaker function when the SA node fails to do so. This dysrhythmia also may occur when the electrical impulses from the SA node fail to reach the AV node because of SA or AV block. It occurs when the rate of depolarization of the sinoatrial node falls below the rate of the atrioventricular node. A junctional escape beat is a delayed heartbeat originating not from the atrium but from an ectopic focus somewhere in the atrioventricular junction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
